本章简要介绍 Python 可视化的基本概念和一些常用的可视化库。
可视化的目的
数据分布:了解数据的分布情况,识别异常值和趋势。
数据关系:探索变量之间的关系,识别相关性和因果关系。
数据模式:识别数据中的模式和规律,帮助进行预测和决策。
数据传达:通过图形化的方式传达数据的含义和故事,帮助观众理解数据。
学习资源
五大扩展包:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/148748125
帮我补充
Python 绘图命令的基本语法和逻辑
file:///D:/Rbook/DSFinance/books/VanderPlas_2023_PDSH_Python_Data_Science_Handbook-2E.pdf#page=281.11,Chap29-35 介绍了很多绘图的语法知识。
常用的可视化库
Matplotlib:最常用的 Python 可视化库,功能强大,支持多种图表类型。
Seaborn:基于 Matplotlib 的高级可视化库,提供更美观的默认样式和更简便的接口。
Plotly:交互式可视化库,支持多种图表类型,适合 Web 应用。
Bokeh:另一种交互式可视化库,适合大数据集和实时数据流。
Altair:基于 Vega-Lite 的声明式可视化库,适合快速创建复杂的图表。
ggplot:基于 Grammar of Graphics 的可视化库,适合统计图表的创建。
Pygal:适合创建 SVG 图表的库,支持多种图表类型。
Folium:用于创建交互式地图的库,适合地理数据可视化。
Geopandas:用于处理地理数据的库,支持空间数据的可视化。
NetworkX:用于创建和可视化网络图的库,适合社交网络分析。
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npfrom matplotlib.patches import Ellipse# Fixing random state for reproducibility 19680801 )= 250 = [Ellipse(xy= np.random.rand(2 ) * 10 ,= np.random.rand(), height= np.random.rand(),= np.random.rand() * 360 )for i in range (NUM)]= plt.subplots()set (xlim= (0 , 10 ), ylim= (0 , 10 ), aspect= "equal" )for e in ells:3 ))
文字标注
实例
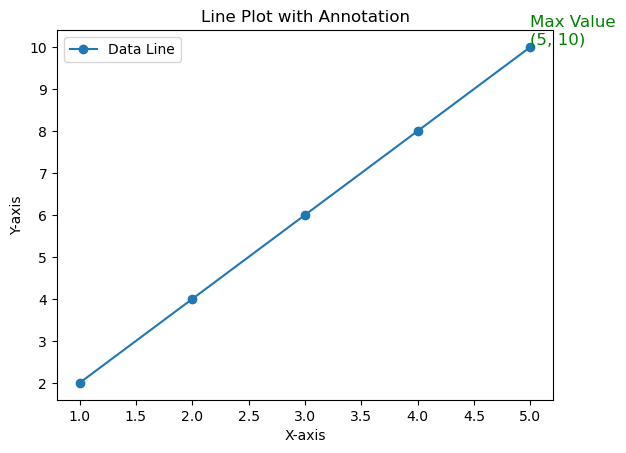
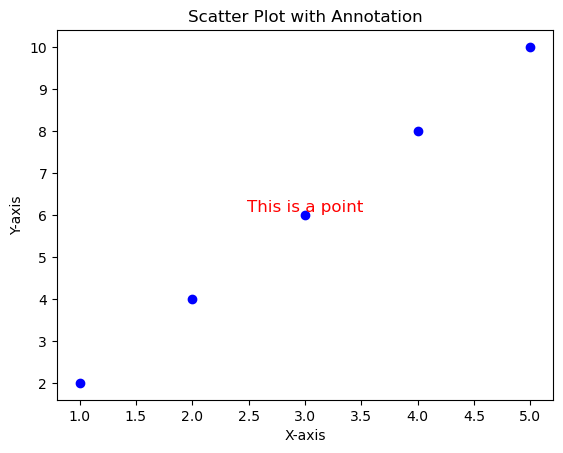
举一个小例子,说明如何在图形上标注说明文字,涉及:字号,颜色,位置等特征的设定
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 创建一个简单的折线图 = 'o' , label= 'Data Line' )# 找到最大值点 = x[- 1 ]= y[- 1 ]# 在最大值点标注说明文字 f'Max Value \n ( { max_x} , { max_y} )' , = 12 , color= 'green' , ha= 'left' , va= 'bottom' )# 设置标题和轴标签 'Line Plot with Annotation' )'X-axis' )'Y-axis' )# 显示图例 # 显示图形
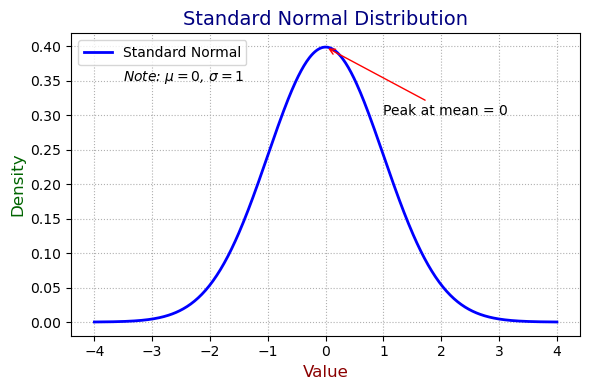
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom scipy.stats import norm# 生成标准正态分布数据 = np.linspace(- 4 , 4 , 500 )= norm.pdf(x, loc= 0 , scale= 1 )# 绘图 = (6 , 4 ))= "Standard Normal" , color= "blue" , linewidth= 2 )# 设置坐标轴标题和主标题 "Value" , fontsize= 12 , color= "darkred" ) # x 轴标题 "Density" , fontsize= 12 , color= "darkgreen" ) # y 轴标题 "Standard Normal Distribution" , fontsize= 14 , color= "navy" , loc= "center" ) # 主标题 # 添加图例 = "upper left" , fontsize= 10 , frameon= True )# 添加注释(note) "Peak at mean = 0" , xy= (0 , norm.pdf(0 )),= (1 , 0.3 ), fontsize= 10 ,= dict (arrowstyle= "->" , color= "red" ))# 添加自定义文字 text - 3.5 , 0.35 , "Note: $ \\ mu = 0$, $ \\ sigma = 1$" ,= 10 , color= "black" , style= "italic" )# 美化 True , linestyle= ":" )
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 创建一个简单的散点图 = [1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]= [2 , 4 , 6 , 8 , 10 ]= 'blue' )# 添加说明文字 3 , 6 , 'This is a point' , fontsize= 12 , color= 'red' , ha= 'center' , va= 'bottom' )# 设置标题和轴标签 'Scatter Plot with Annotation' )'X-axis' )'Y-axis' )# 显示图形